Improve your home
23 Aug 2022
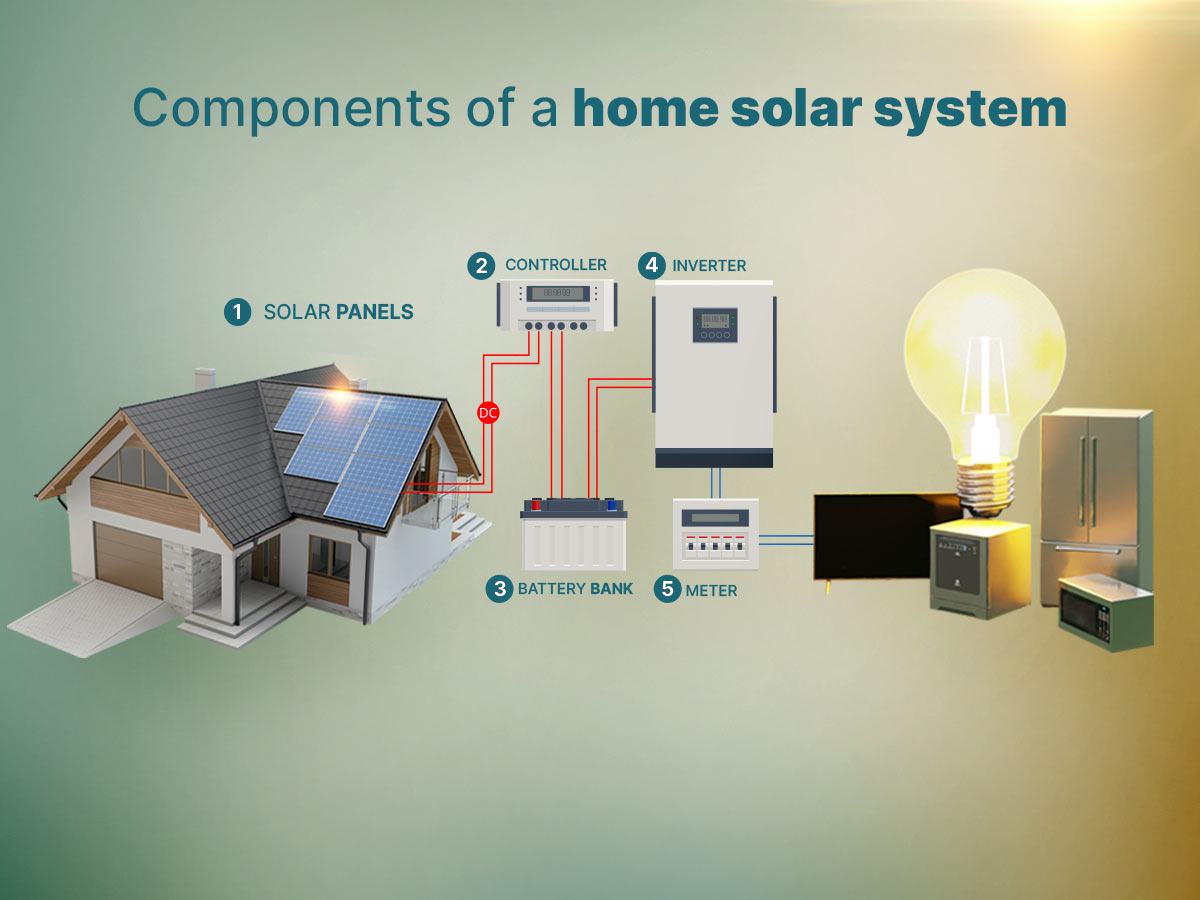
Components of a home solar system
While solar panels are an essential component of a home solar system, you will need several other elements to collect energy from the sun and convert it into electricity you can use in your home.
Understanding how the various components of a solar system fit together will help you choose the best solution for your home and family.
- Solar panels: When we think of solar systems, solar panels are the first thing that comes to mind. The panels are made up of photovoltaic cells, which absorb energy from the sun and convert this into direct current (DC) electricity. The most common types of technology offered for home solar systems are monocrystalline, polycrystalline and thin-film solar panels. The number of solar panels you can mount on your roof depends on cardinal direction, roof area, slope and horizontal irradiance. Visit LookSee’s Solar Score to discover what you can expect from a solar solution on your property.
- Battery charge controller: Most solar systems include a battery bank to ensure homes can store converted electricity for use outside of sunlight hours. As batteries also operate on DC power, it is more effective to place your battery bank before the inverter in your solar solution. The battery charge controller regulates the flow of electricity from the panels to the battery system, ensuring batteries are not damaged through overcharging or discharging.
- Battery bank: Batteries may not be the first thing you think of when considering a solar system for your home, but this is not an area you want to skimp on. The most popular options for battery technology include lead-acid, lithium-ion and lithium iron phosphate. While lower prices may be tempting, be sure to speak to your provider about the differences in efficiency, degradation and cycle life, as your battery bank will be the backbone of your system.
- Inverter: In order for your home to be able to make use of your solar and battery-stored power, it needs to be converted from DC to alternating current (AC) electricity. This is the role that the inverter plays in your solar system. It’s important to bear in mind that inverters are limited in the amount of electricity they can convert at the same time, so make sure the inverter you choose allows you to add solar panels or increase the amount of power your home draws further down the line.
- Electrical board: The output from your inverter is then wired into the main electrical board of your home for household use. There are 2 options that can be used in this regard. The first is a hybrid model where you use your solar power and switch over to grid-supplied power when this runs out. The other option is to go completely off the grid by disconnecting from the utility supply. All work on a home’s electrical board must be done by a qualified and registered electrician and an electrical certificate of compliance must be issued after the work is complete.
Looking for instant solar quotes with a free consultation?
LookSee offers a full solar journey coupled with a Savings Guarantee based on your minimum saving expectations over 6 months and a once-off R2 000 cashback if savings are not met.
Related articles:









